Development of a Low-Cost Multipurpose Autonomous Navigation Robot
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the need for contactless solutions. This project presents the design and development of a low-cost multipurpose autonomous navigation robot. The proposed system utilizes a Lidar sensor in conjunction with a Pi camera to perform Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), enabling the robot to autonomously navigate dynamic environments. Additionally, the robot is equipped with capabilities for object detection, person following, and real-time surveillance, making it suitable for UV sanitization, food and medicine delivery, and teleoperation.
Introduction
Modern autonomous robots face high initial costs, limiting their widespread use. Advances in open-source platforms like ROS have paved the way for developing low-cost robotic systems. This work addresses the challenge of mapping unknown environments through the integration of affordable sensors and robust SLAM algorithms. By leveraging a Lidar sensor and a low-cost Pi camera, the system achieves reliable mapping and navigation, making it a viable solution for various applications during and beyond the pandemic.
Methodology
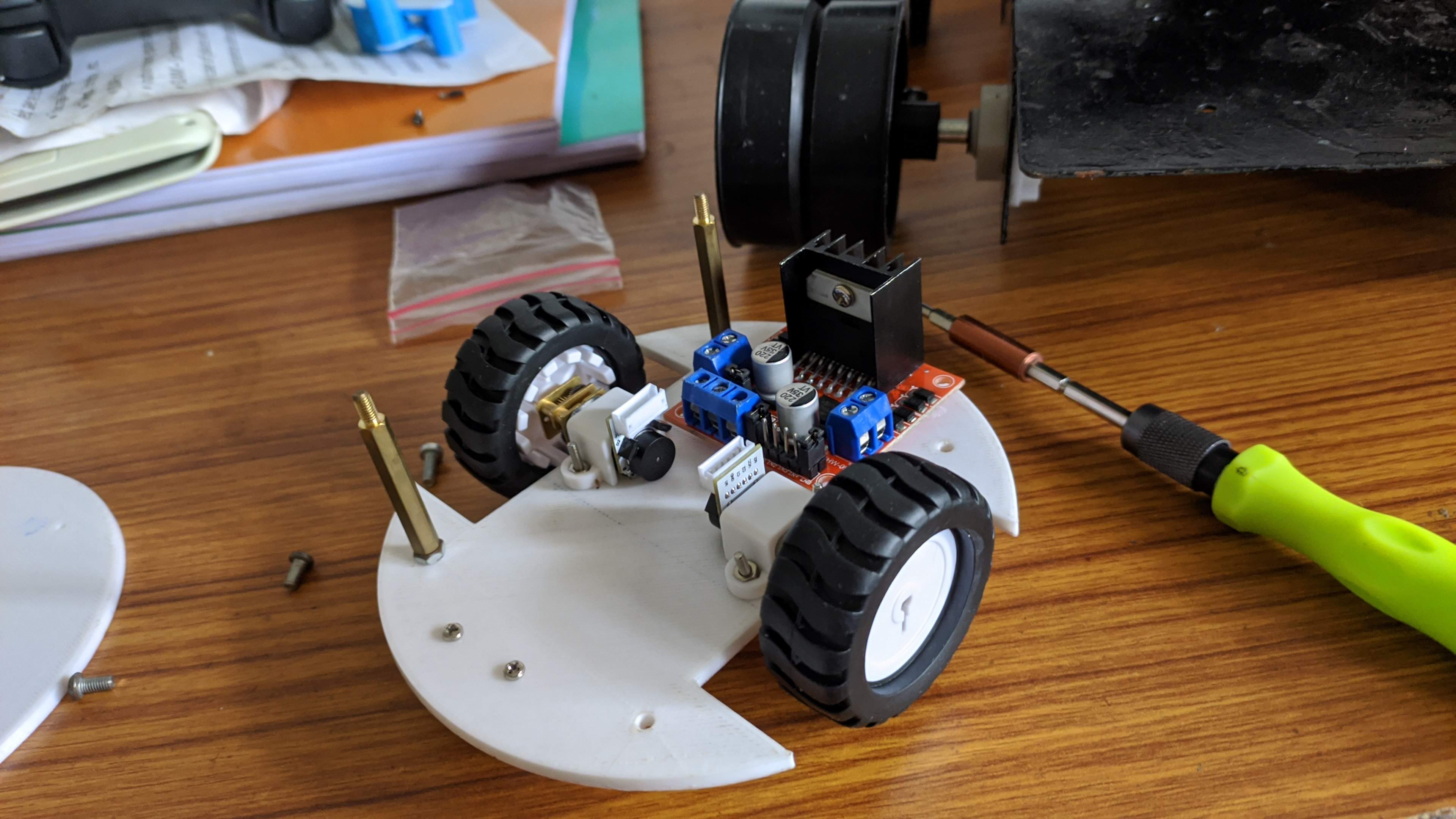
The development process began with detailed design and simulation studies in Fusion360. The CAD model was then converted to a URDF format and refined through 3D printing using PLA material. Key hardware components include:
- Main Chassis: Four disk structures (120 mm diameter, 3 mm thickness) form the primary body.
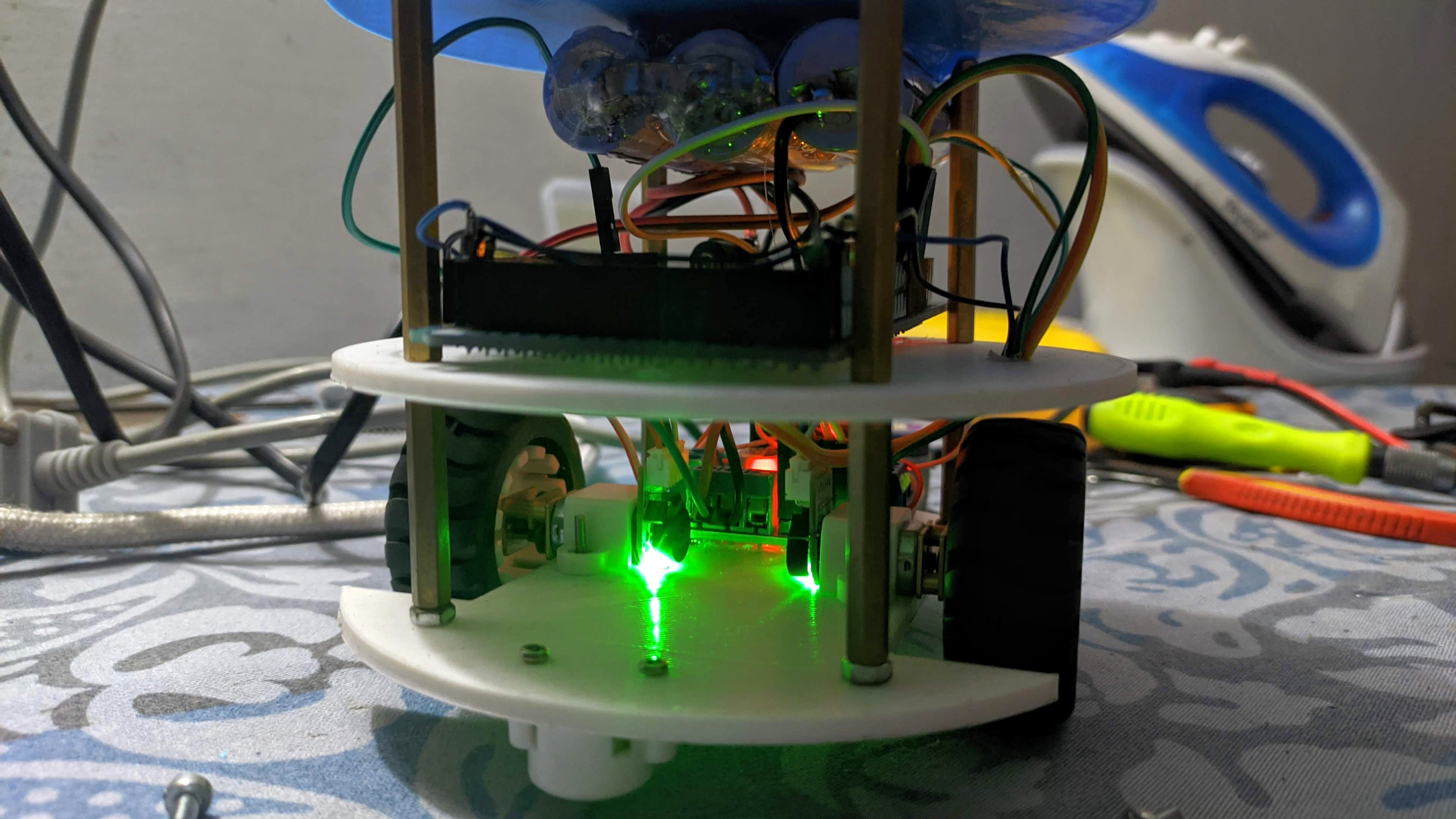
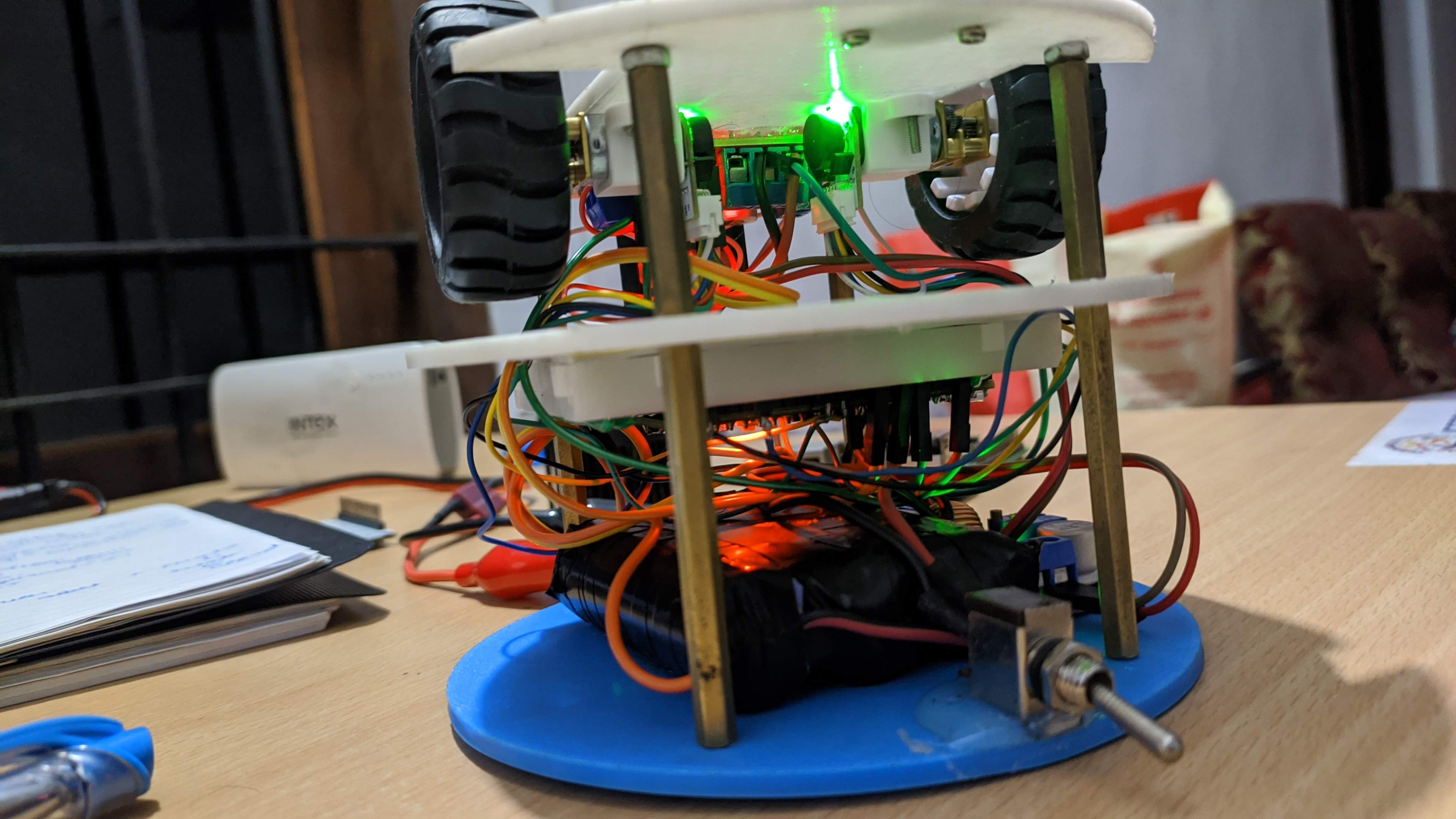
- Bottom Deck: Houses DC motors with encoders and a motor driver for movement.
- Upper Deck: Contains low-level control equipment (Teensy 3.6 microcontroller) and an MPU-6050 IMU, used for pose estimation.
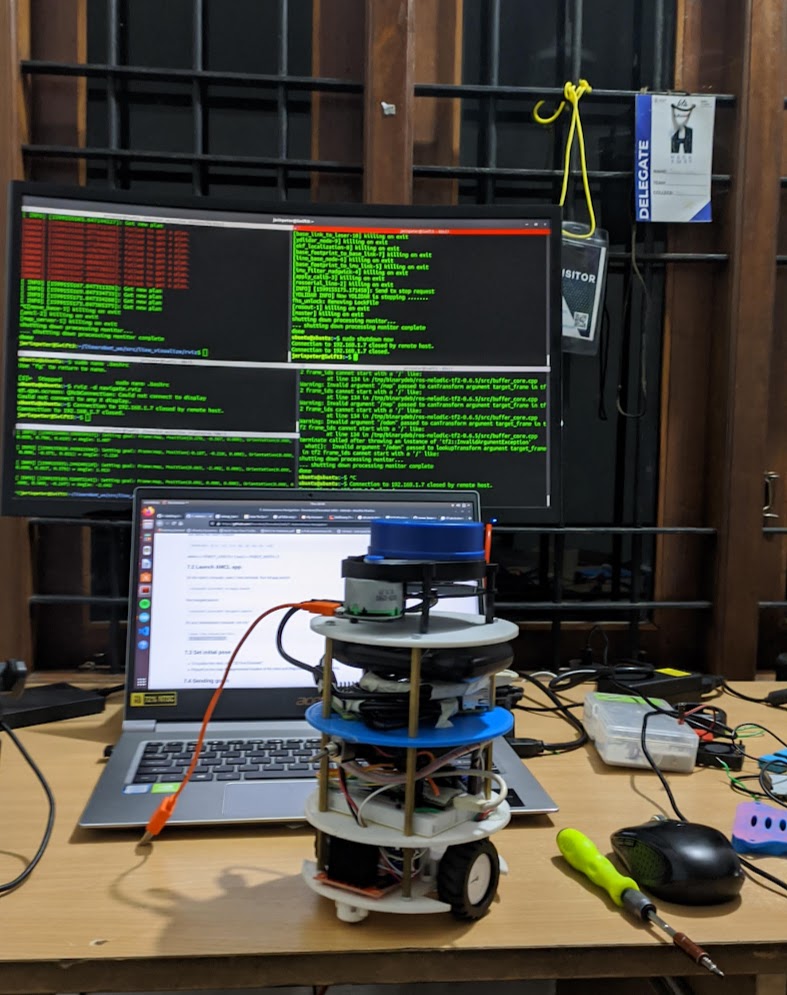
- Sensor Suite: A wide-angle Pi camera provides real-time video for surveillance, and the Lidar sensor facilitates precise mapping.


Results and Discussion
Simulation studies in Gazebo and subsequent real-world testing confirmed that the robot can autonomously map its environment and navigate to predefined goal locations. The integration of Lidar and the Pi camera provided robust data for the SLAM algorithms, enabling accurate localization even in dynamic settings. Experimental results demonstrated that the system can reliably perform tasks such as obstacle avoidance, object recognition, and person following.
Conclusion
The developed low-cost multipurpose autonomous navigation robot offers a practical solution for contactless operations. With its affordable sensor suite and robust SLAM implementation, the robot can be deployed for UV sanitization, delivery of food and medicine, and teleoperated surveillance. Future enhancements will focus on refining the object detection algorithms and integrating additional sensors to further improve navigation accuracy and operational reliability.
Future Scope
- Integration with advanced ROS-based path planning and localization modules.
- Implementation of enhanced object recognition and person following using machine learning frameworks.
- Expansion of the sensor suite to include additional environmental monitoring tools.
- Scaling the prototype for larger, commercial-grade applications.